Comparing Traditional and VR-Based Laparoscopic Tools: Innovations in Surgical Training and Education
Laparoscopic surgery, known for its minimally invasive approach, has revolutionized the field of surgery by allowing procedures to be performed through small incisions. This technique minimizes patient recovery time and reduces postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery. In the field of laparoscopic surgery, both traditional training and VR-based training rely on a range of specialized tools and technologies. However, the way these tools are used and their effectiveness in training can vary significantly between the two approaches.
Traditionally, laparoscopy has relied on physical tools and equipment, while recent advancements have introduced Virtual Reality (VR)-based laparoscopy as a novel educational approach. Explore the tools utilized in traditional laparoscopic training and their contrast with those used in VR-based laparoscopic training.
Tools in Traditional Laparoscopic Training
- Physical Models (Simulators and Cadavers)

2.Basic Laparoscopic Instruments
- Animal Models and Cadavers: Traditional training often begins with the use of animal models or human cadavers to simulate real surgical environments. These models provide a tactile experience that closely mimics the human anatomy but come with ethical considerations, high costs, and limited availability.
- Box Trainers: Box trainers are one of the most common tools used in laparoscopic training. These simple setups consist of a physical box with strategically placed ports through which surgeons practice manipulating real laparoscopic instruments. Inside the box are various training models, such as synthetic organs, that mimic surgical tasks like suturing, knot-tying, or cutting.
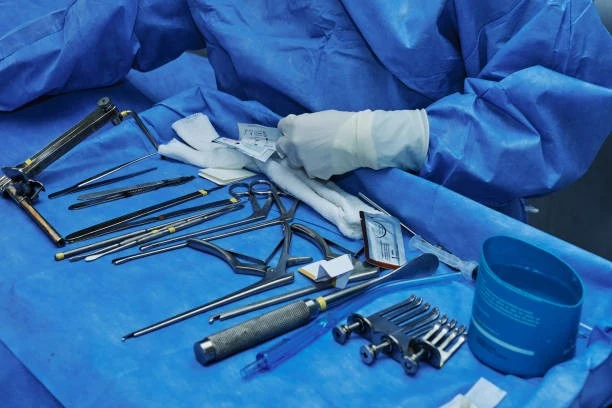
3.Video Equipment
- Laparoscopic Camera: A key tool in traditional laparoscopy is the laparoscopic camera, which provides a visual of the surgical field on a 2D monitor. The training involves learning how to interpret and manipulate this camera view effectively.
- Monitors and Light Sources: The laparoscopic camera transmits images to a high-resolution monitor, which provides the surgeon with a detailed view of the surgical field. The light source attached to the laparoscope illuminates the area, ensuring that the camera captures clear and bright images.

4.Insufflator
An insufflator is used to introduce carbon dioxide (CO2) into the abdominal cavity, creating a working space by distending the abdomen. This inflation allows better visibility and access to the surgical area.
Limitations: While these tools provide hands-on experience and help trainees develop basic skills, they often lack the complexity and variability found in real surgical situation. Training with them in traditional settings often lacks the context of a real procedure and trainees may struggle with the lack of real-time feedback and limited exposure to diverse surgical scenarios.
Tools in VR-Based Laparoscopic Training
- Immersive VR Headsets: It is the foundation of VR-based training, providing a fully immersive 3D environment that replicates the surgical field. Modern VR headsets offer high-resolution displays and wide fields of view, allowing trainees to experience the surgery as if they were physically present in the operating room.

2.Virtual Laparoscopic Instruments
In VR-based training, laparoscopic instruments are replicated digitally. These virtual tools mirror their real-world counterparts, allowing trainees to practice techniques without the need for physical instruments. The digital tools include:

- Virtual Graspers and Forceps: Simulated tools for manipulating virtual tissues.
- Virtual Scissors: Used for cutting in the virtual environment.
- Virtual Needle Holders: For practicing suturing techniques.
- Advanced VR Simulators: VR systems come with a range of training modules and simulations that cover various surgical procedures and scenarios. These modules provide step-by-step guidance and performance metrics to help trainees improve their skills. Key features include:
- Laparoscopic VR Simulators: These are comprehensive training systems that include software capable of simulating a wide range of surgical scenarios. They offer interactive, 3D models of the human anatomy that trainees can manipulate in real-time, providing a dynamic and engaging learning experience.
- Performance Metrics: Immediate feedback on performance, including accuracy and technique, helps trainees refine their skills.
Benefits: Unlike traditional tools, VR simulators allow for repetitive practice without the risk of patient harm. They can also simulate rare or complicated cases, providing trainees with experience in a broader range of scenarios than they might encounter in a traditional training environment.
At Inion VR, we’re redefining surgical education with our innovatory virtual reality training solutions. Our advanced VR-based laparoscopic training systems provide an immersive, interactive environment where you can perfect your skills, practice complex procedures, and receive real-time feedback—all without the limitations of traditional training methods.
Ready to experience the next level of surgical education and advance your skills? Connect with Inion VR today to discover how our innovative training solutions can transform your surgical practice. Visit our website or contact us for a personalized demonstration!
- Data analytics and Performance Tracking
Advanced VR systems often include data analytics tools that track and analyse the trainee’s performance. Metrics such as precision, speed, and error rates are recorded, providing insights into areas for improvement. This data helps educators tailor training programs to individual needs and track progress over time.
- Simulated Operating Environments
The VR environment is designed to closely mimic a real operating room, including realistic visuals, sounds, and instrument responses. This immersive experience helps trainees adapt to
the sensory and spatial aspects of laparoscopic surgery, enhancing their overall training experience.
The tools used in traditional laparoscopic training have laid the foundation for developing essential surgical skills, but they come with limitations that can hinder the depth and breadth of training. VR-based training with advanced features offers a more comprehensive and effective approach. By replicating real surgical environments and providing a platform for unlimited, risk-free practice, VR is transforming the surgical training, leading to improved surgical outcomes and enhanced patient safety.


